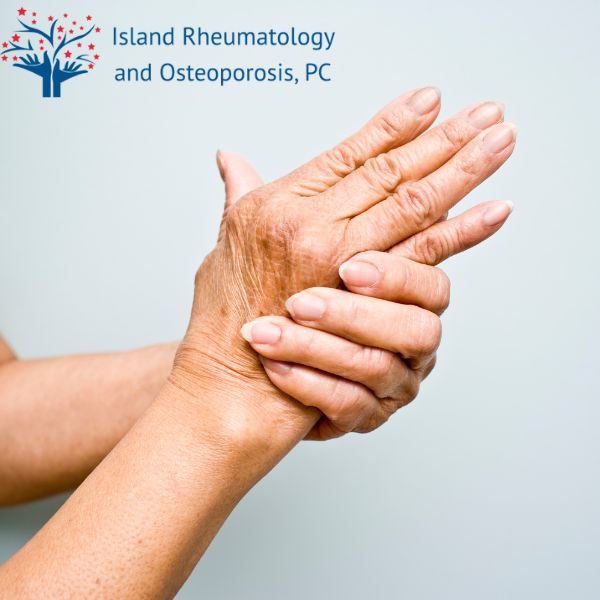
03 Mar Understanding the Different Types of Arthritis
Arthritis, a term often associated with joint pain and stiffness, encompasses a myriad of different conditions. Contrary to popular belief, it is not a single disease but a collection of over 100 types of joint issues that affect people of all ages. The variations in arthritis can make it challenging to understand and manage effectively. In this article, we will delve into the most common types of arthritis, their symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Overview: Osteoarthritis is the most prevalent form of arthritis, often referred to as “wear and tear” arthritis. It primarily affects the cartilage—the protective tissue cushioning the ends of bones in joints.
Symptoms: People with OA typically experience joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. The pain is often worse after periods of inactivity or towards the end of the day.
Causes: OA is generally caused by the degeneration of cartilage due to aging. However, factors such as obesity, joint injuries, and genetics can increase the risk.
Treatment: Management includes lifestyle changes like weight loss and exercise, physical therapy, pain relief medications, and in severe cases, joint replacement surgery.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Overview: Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes the immune system to mistakenly attack the synovium—the lining of the membranes surrounding the joints.
Symptoms: RA symptoms include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and redness. It commonly affects smaller joints first, such as those in the hands and feet. RA can also cause systemic symptoms like fatigue and fever.
Causes: The exact cause is unknown, but genetics, environmental factors, and hormonal changes are believed to play a role.
Treatment: Treatment for RA focuses on controlling symptoms and slowing the progression of the disease. It includes medications like disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologics, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery.
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
Overview: Psoriatic arthritis is a type of inflammatory arthritis that occurs in some people with psoriasis—a condition that causes red, scaly skin patches.
Symptoms: PsA can affect any joint and its symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. It can also cause changes in the nails, such as pitting or separation from the nail bed.
Causes: The exact cause is unknown, but genetics and environmental factors play a significant role. The immune system attacking healthy cells and tissue is believed to be a contributing factor.
Treatment: Treatment options for PsA include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), DMARDs, biologics, and physical therapy. Managing skin symptoms through topical treatments is also crucial.
Gout
Overview: Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness, and tenderness in joints, often the big toe.
Symptoms: Symptoms include intense joint pain, swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected area. These attacks can occur suddenly, often waking people up in the middle of the night.
Causes: Gout is caused by the accumulation of urate crystals in the joint, which results from high levels of uric acid in the blood. Factors contributing to gout include diet, obesity, certain medical conditions, and medications.
Treatment: Treatment focuses on managing pain and inflammation during attacks and preventing future attacks. This includes medications like NSAIDs, colchicine, and corticosteroids. Long-term management involves lifestyle changes and medications to lower uric acid levels.
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)
Overview: Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine, causing inflammation in the spinal joints.
Symptoms: Symptoms include chronic pain and stiffness in the lower back and hips, especially in the morning and after periods of inactivity. Over time, AS can cause the vertebrae to fuse, leading to a loss of flexibility.
Causes: The exact cause is unknown, but genetics play a significant role, particularly the HLA-B27 gene.
Treatment: Treatment includes medications to reduce inflammation and pain, physical therapy, and exercises to maintain flexibility and posture. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
Juvenile Arthritis
Overview: Juvenile arthritis is an umbrella term for several types of arthritis affecting children under the age of 16.
Symptoms: Symptoms include joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. It can also cause eye inflammation, fever, and fatigue.
Causes: The causes of juvenile arthritis are not well understood but are believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Treatment: Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation, managing pain, and improving function. It includes medications, physical therapy, and a healthy lifestyle.
Contact Us
Understanding the different types of arthritis is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. While arthritis can significantly impact quality of life, early detection and comprehensive management can help people live active and fulfilling lives. If you suspect you have arthritis, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.

