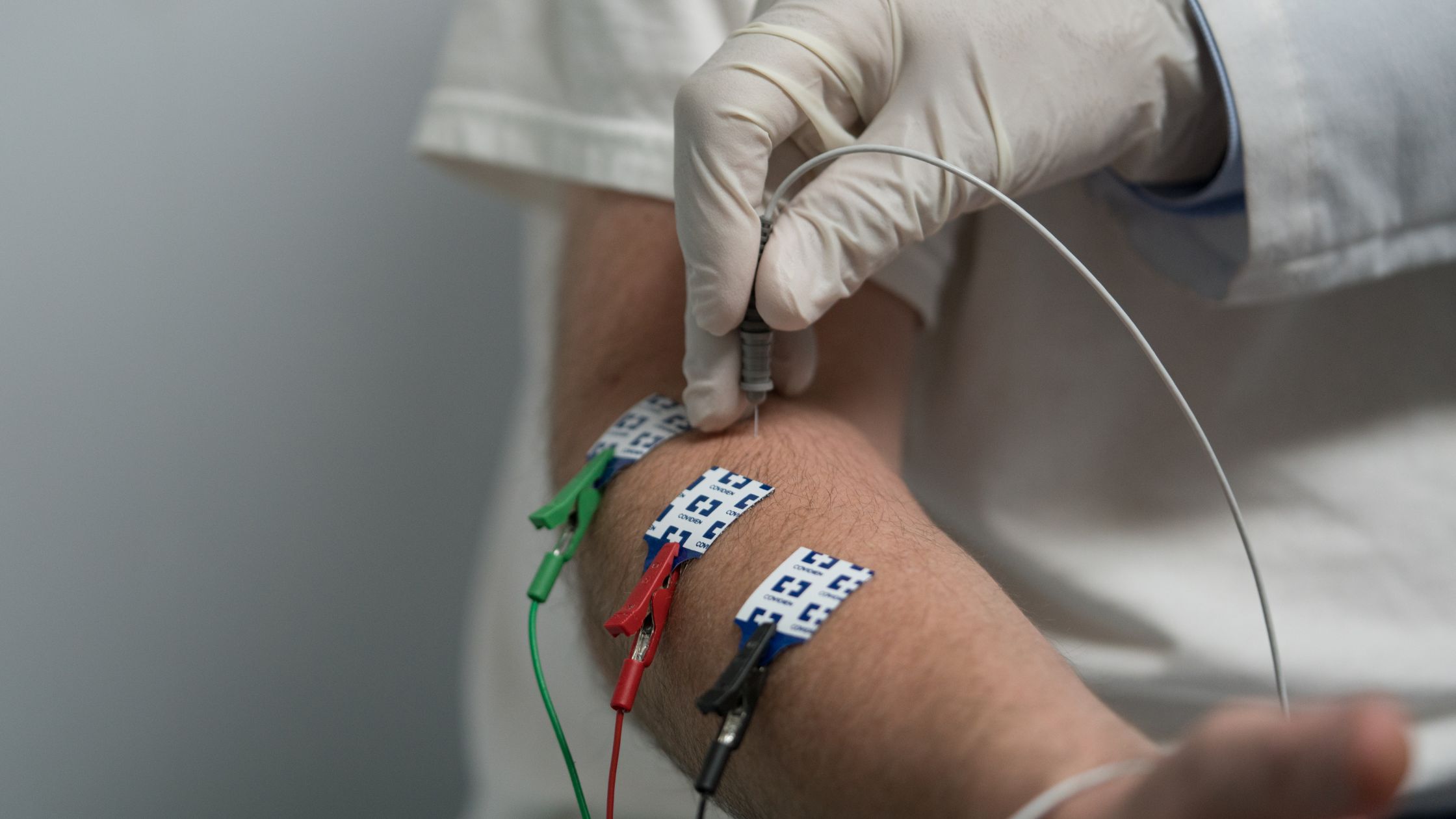
22 Apr Deciphering EMG Results: Unraveling the Secrets of Nerve and Muscle Function
Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) are diagnostic tools that provide valuable insights into the functioning of nerves and muscles. These tests are often employed to diagnose various neuromuscular disorders and injuries, aiding healthcare providers in crafting effective treatment plans. However, interpreting the results of EMG/NCS tests can be challenging for patients, as they may not fully understand what the findings mean and their implications. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the intricacies of interpreting EMG/NCS results, distinguish between normal and abnormal findings, explore the significance of discussing outcomes with healthcare providers, and stress the importance of follow-up in monitoring progress and adjusting treatment plans.
Understanding the Findings:
Upon receiving the results of an EMG/NCS test, patients may be perplexed by the jargon-filled report. However, breaking down these findings into comprehensible terms is crucial for understanding one’s nerve and muscle health. In essence, EMG measures the electrical activity of muscles, while NCS evaluates the speed and strength of nerve signals.
Normal EMG results typically exhibit a pattern of electrical activity indicative of healthy muscle function. Conversely, abnormal EMG readings may suggest underlying neuromuscular disorders such as peripheral neuropathy, myopathy, or nerve compression. NCS results, on the other hand, may reveal abnormalities in nerve conduction velocities and amplitudes, signaling potential nerve damage or dysfunction.
Differentiating Normal vs. Abnormal:
Distinguishing between normal and abnormal EMG/NCS findings is paramount in assessing nerve and muscle function. Normal results generally indicate that nerves and muscles are functioning within expected parameters, without any signs of pathology or impairment. Abnormal results, on the other hand, may indicate a range of conditions, including nerve entrapment syndromes, neuropathies, muscular dystrophies, or motor neuron diseases.
For instance, in cases of carpal tunnel syndrome, an entrapment neuropathy, EMG/NCS may reveal reduced nerve conduction velocities across the median nerve, along with abnormal muscle responses in the affected hand muscles. Similarly, in conditions like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), EMG/NCS findings may show signs of denervation and muscle atrophy, reflecting the progressive degeneration of motor neurons.
Discussing Outcomes with Healthcare Providers:
Upon receiving EMG/NCS results, patients should schedule a follow-up appointment with their healthcare provider to discuss the implications of the findings. This discussion serves as an opportunity to gain a deeper understanding of one’s condition, explore available treatment options, and devise a comprehensive management plan.
Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in interpreting EMG/NCS results and guiding patients through the diagnostic and treatment process. They can provide valuable insights into the significance of abnormal findings, recommend further diagnostic tests if necessary, and prescribe appropriate medications or therapies to alleviate symptoms and manage the underlying condition.
Moreover, open communication between patients and healthcare providers fosters a collaborative approach to care, empowering patients to actively participate in decision-making regarding their treatment journey. Patients should feel comfortable asking questions, expressing concerns, and seeking clarification on any aspects of their EMG/NCS results and recommended treatment plan.
The Importance of Follow-Up At Island Rheumatology:
Following the initial discussion of EMG/NCS results, patients should adhere to scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor their progress and adjust treatment plans as needed. Regular follow-up visits allow healthcare providers to track changes in nerve and muscle function over time, assess the efficacy of treatment interventions, and make necessary adjustments to optimize patient outcomes.
Additionally, follow-up appointments provide an opportunity for patients to discuss any new or worsening symptoms, address concerns or side effects related to treatment, and receive ongoing support and guidance from their healthcare team. Consistent monitoring and proactive management are essential components of comprehensive neuromuscular care, ensuring that patients receive timely interventions to minimize disease progression and enhance quality of life.
In conclusion, interpreting EMG/NCS results requires a nuanced understanding of nerve and muscle physiology, as well as collaboration between patients and healthcare providers. By deciphering the findings, distinguishing between normal and abnormal results, discussing outcomes with healthcare providers, and prioritizing follow-up care, patients can navigate their diagnosis and treatment journey with confidence and empowerment. Ultimately, proactive management and ongoing support are integral to achieving optimal outcomes and maintaining overall well-being in individuals with neuromuscular disorders.

